In recent years, U.S. maternal mortality has emerged as a pressing public health crisis, underscoring alarming trends in pregnancy-related deaths. Despite advancements in healthcare, the U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, signaling significant gaps in maternal health services. A recent study highlights that more than 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, emphasizing the urgent need for improved prenatal care and extended postpartum support. Disparities persist, particularly affecting marginalized racial and ethnic groups, further exacerbating healthcare disparities across the nation. Addressing U.S. maternal mortality requires a comprehensive approach to enhance postpartum care, ensure equitable access to services, and implement effective policies to safeguard maternal health.
The issue of maternal health in America is characterized by alarming statistics surrounding pregnancy-related fatalities. Known informally as maternal death rates, the troubling rise in these fatalities reflects broader systemic challenges within the nation’s healthcare framework. Many expectant mothers face significant barriers to receiving adequate prenatal support and follow-up care post-delivery, which is crucial for mitigating potential risks during and after pregnancy. Racial and socioeconomic disparities compound these challenges, creating varied healthcare experiences across different demographics. As we delve deeper into understanding maternal outcomes, it becomes increasingly clear that comprehensive strategies are required to bridge the gaps in care and ensure the well-being of mothers nationwide.
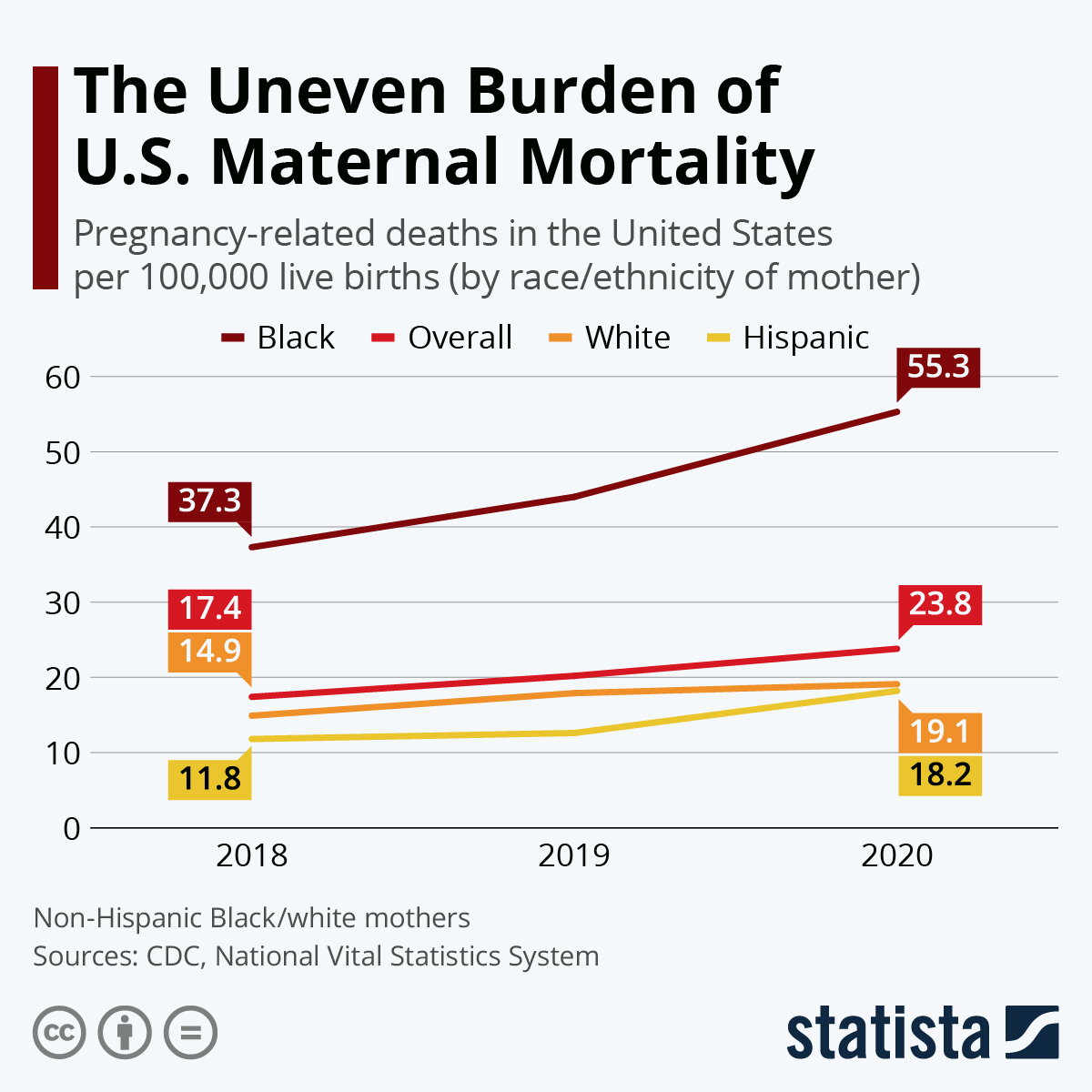
Understanding U.S. Maternal Mortality Rates
The alarming rise in U.S. maternal mortality rates has positioned the nation at the forefront of discussions regarding maternal health globally. With recent data indicating a continuous uptick in pregnancy-related deaths, it becomes essential to unpack the factors contributing to this crisis. Key issues such as poor prenatal care access, healthcare disparities across different demographic groups, and the prevalence of chronic illnesses like hypertension among younger reproductive-age women play substantial roles in exacerbating maternal risk.
Additionally, the disparities in maternal mortality are stark when comparing different racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women are disproportionately affected, exhibiting significantly higher mortality rates compared to white women. This discrepancy demonstrates the urgent need for targeted public health strategies and policies that can effectively address the specific needs of various communities, ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare throughout pregnancy and beyond.
The Importance of Prenatal and Postpartum Care
Prenatal care is critical in monitoring the health of both mother and baby, aiming to prevent complications that could lead to pregnancy-related deaths. A strong emphasis on regular check-ups, screenings, and education during pregnancy can mitigate risks significantly. However, it is evident that the U.S. healthcare system has not prioritized these essential services, leading to increased morbidity and mortality rates among vulnerable populations.
Postpartum care is equally vital, as many pregnancy-related deaths occur during the year following childbirth. The need for comprehensive support that extends well beyond the traditional six-week check-up is highlighted by concerning trends in late maternal deaths. Continuous healthcare access can aid in the management of chronic conditions and mental health, both critical components in reducing overall maternal mortality and improving health outcomes for mothers.
Healthcare Disparities Impacting Maternal Health
Significant healthcare disparities contribute to the rising maternal mortality rates in the U.S. Many women, particularly those from minority or low-income backgrounds, face barriers in accessing quality maternal health services. These may include financial constraints, lack of insurance coverage, and geographic limitations, which often result in inadequate prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing these disparities requires comprehensive healthcare reforms to enhance accessibility and affordability of services for all women.
Moreover, societal factors such as systemic racism and discrimination within healthcare settings further exacerbate these disparities. Disparities in treatment quality and outcomes among different racial groups highlight the need for a concerted effort to educate healthcare providers about implicit biases and to implement standardized care protocols. Effective training and policy changes are crucial in moving towards a more equitable healthcare system, ensuring that all women receive the care they need during pregnancy.
The Role of Chronic Conditions in Maternal Mortality
Chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease have increasingly become significant contributors to maternal mortality in the U.S. The study indicates that these conditions disproportionately affect younger women, raising concerns about their long-term health management. Awareness and early intervention are crucial to improving maternal health outcomes, yet many women lack access to necessary screenings and treatments pre-pregnancy.
To combat this issue, public health initiatives need to focus on not just pregnancy care but also overall reproductive health prior to conception. Programs aimed at preventing and managing chronic diseases can play a pivotal role in reducing risks during pregnancy and helping women lead healthier lives post-delivery. Collaborative efforts between obstetricians and primary care providers are essential in achieving holistic health management for women of childbearing age.
Innovative Solutions for Improving Maternal Health
To tackle the issue of rising maternal mortality rates, innovative solutions must be embraced. This includes enhancing digital health technologies that facilitate better communication between providers and patients, allowing for timely interventions when complications arise. Mobile health applications, telemedicine, and remote monitoring can help bridge gaps in care particularly for those living in rural or underserved areas.
In addition to technology, community-based interventions tailored to the specific needs of populations at risk can significantly enhance maternal health outcomes. Programs that provide education, resources, and supportive networks empower women to take control of their health throughout their pregnancy journey. Collaborating with local organizations and stakeholders can help ensure that these interventions are both culturally relevant and effective.
Policy Changes Needed to Reduce Maternal Mortality
The rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. signal an urgent need for policy reforms aimed at improving maternal health services. Comprehensive approaches that address healthcare accessibility, affordability, and quality are necessary at both state and national levels. Policymakers must prioritize funding for maternal health programs and initiatives that bridge the care gap, particularly in underserved communities.
Moreover, integrating maternal health considerations into broader public health strategies is essential. By prioritizing maternal health in national health agendas, the government can ensure that policy decisions are informed by the real needs of mothers and families, establishing frameworks for systematic change. Investing in maternal health not only benefits the individual but promotes healthier generations to come, paving the way for a sustainable future.
Addressing the Impact of COVID-19 on Maternal Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound influence on maternal health, exacerbating already existing health disparities and leading to a spike in pregnancy-related deaths. As health systems became overwhelmed, access to routine prenatal and postpartum care diminished, leaving many women without essential support during pregnancy and after childbirth. The pandemic has highlighted the need for adaptable healthcare systems that can withstand crises and continue to prioritize maternal health.
To mitigate the impact of current and future public health emergencies, it is crucial to learn from the pandemic experience. Establishing flexible healthcare policies that promote telehealth options, extended postpartum support, and emergency care access can help safeguard maternal health during unforeseen events. Continuous evaluation and adjustment of health systems are key to protecting the most vulnerable populations and enhancing resilience in maternal health care.
Community Support Initiatives for Maternal Health
Community support initiatives play a vital role in enhancing maternal health outcomes, offering education, resources, and emotional support tailored to the needs of new mothers. Programs that connect women with local health resources, peer support groups, and educational workshops can empower mothers to navigate the complexities of pregnancy and postpartum recovery more effectively. Building community bonds fosters an environment where mothers feel supported, understood, and informed.
These initiatives also serve as catalysts for change in addressing healthcare disparities. By empowering community leaders and organizations to take the helm, local solutions can be devised to combat maternal mortality effectively. Furthermore, integrating traditional practices with modern healthcare principles can create culturally relevant approaches that resonate with diverse populations, enhancing engagement and improving health outcomes for mothers.
The Future of Maternal Health in America
Looking ahead, the future of maternal health in America hinges on our ability to learn from current trends and invest meaningfully in maternal care systems. As the studies reveal concerning statistics around maternal mortality, there is a pressing need to innovate and reform healthcare delivery to meet the complex challenges faced by mothers. A focus on addressing healthcare disparities and chronic diseases can lead to improved maternal outcomes in the long term.
Moreover, fostering a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations is paramount. By creating a unified front, stakeholders can leverage resources, share best practices, and implement strategies that prioritize maternal health. Ensuring systemic changes are embraced will help pave the way for healthier pregnancies and ultimately lead to lower maternal mortality rates, signaling a significant shift in America’s approach to maternal care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
In the U.S., the leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths include cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and infection. Cardiovascular disease has recently become the foremost cause, accounting for over 20% of such deaths. This alarming trend highlights the need for improved maternal health during pregnancy and postpartum care.
How does U.S. maternal mortality compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with significant increases observed from 2018 to 2022. This heightened rate indicates systemic issues in maternal health and healthcare access, including disparities in care received by different racial groups.
What role do healthcare disparities play in U.S. maternal mortality?
Healthcare disparities significantly contribute to U.S. maternal mortality, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. Women of color, especially American Indian and Alaska Native women, experience disproportionately high pregnancy-related deaths due to inequities in healthcare access, treatment quality, and social determinants of health.
Why is postpartum care crucial for reducing maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Postpartum care is essential in addressing U.S. maternal mortality as nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur beyond 42 days postpartum. Comprehensive support during the full year after delivery can mitigate risks and improve long-term maternal health outcomes.
What solutions are suggested to improve U.S. maternal health and reduce mortality rates?
To enhance U.S. maternal health and decrease mortality rates, researchers recommend increased investment in public health infrastructure, innovative care solutions during pregnancy, addressing state-level policy differences, and expanding the focus on comprehensive postpartum care.
How can racial disparities in maternal health be addressed in the U.S.?
Addressing racial disparities in U.S. maternal health requires targeted policies aimed at healthcare access, anti-bias training for providers, and community-based interventions that promote equitable care for all racial groups during pregnancy and postpartum.
What was the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on U.S. maternal mortality rates?
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has had a concerning impact on U.S. maternal mortality rates, with a significant increase in 2021. This trend underscores the need for improved healthcare systems and prenatal care to support pregnant individuals, particularly during health crises.
What trends have been observed in maternal health data since 2018?
Since 2018, data indicates a troubling rise in maternal mortality rates, showing increases across all age groups, especially among women aged 25 to 39. This trend points to a growing prevalence of chronic health conditions impacting pregnancy outcomes and highlights the ongoing need for enhanced maternal health strategies.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Increasing Maternal Mortality | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income countries, which have been rising since 2018, with 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births reported in 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable, highlighting a failure in healthcare provision and policy. |
| Significant Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates at 106.3 per 100,000 live births, followed by non-Hispanic Black women (76.9) and white women (27.6). |
| Impact of Cardiovascular Disease | Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of cases, particularly affecting women aged 25 to 39. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year postpartum) account for nearly a third of all maternal deaths, indicating a need for better postpartum care. |
| Need for Healthcare Reform | Investments are needed to enhance prenatal care and the postpartum period, addressing state-level disparities in maternal health outcomes. |
Summary
U.S. maternal mortality remains a significant public health crisis, with preventable deaths disproportionately affecting women of color. To address these alarming rates, it is essential to focus on improving healthcare systems, enhancing prenatal and postpartum care, and addressing the systemic inequities that persist within the maternal health framework.