Sugar addiction is a growing concern in today’s society, fueled by the prevalence of processed foods rich in added sugars. Many people experience intense sugar cravings, which can lead to compulsive eating behaviors similar to those seen with addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine. The health effects of sugar, especially from ultra-processed foods, are significant and can contribute to a cycle of increased sugar consumption that feels difficult to escape. While sugar is not classified as an addictive substance in the same way drugs or alcohol are, the psychological and physiological impacts are undeniable and can create dependency-like symptoms. To combat this issue, it’s vital to be aware of the amount of sugar in our diets and to make conscious choices about the foods we consume.
The phenomenon of sweet cravings poses questions about our dietary habits and our relationship with common food ingredients. Many refer to this behavior as sugar dependency or even sweet tooth addiction, which signifies the consuming desire for sugary items. In recent discussions, experts have emphasized the drawbacks of excessive sugar intake from various sources, especially ultra-processed options laden with unhealthy fats and additives. Understanding these effects can help us address our habitual sugar consumption and its potential role in our overall health, particularly in terms of mental clarity and emotional well-being. By recognizing the distinction between essential nutrients and overly sweetened products, we can strive for a more balanced and health-conscious approach to our diets.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Impacts
Sugar cravings are a common phenomenon that many people experience, often leading to overconsumption of sugary foods. These cravings can be triggered by various factors such as emotional stress, dietary habits, and even the types of foods we consume regularly. When individuals regularly eat ultra-processed foods rich in sugar, their bodies may come to expect these substances, increasing the frequency and intensity of cravings. This can create a cycle where the urge to consume sugar overrides one’s natural hunger cues, leading to compulsive eating behaviors.
Moreover, the health effects of sugar are significant; excessive sugar consumption can lead to a variety of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The body’s reaction to high sugar intake can be compared to that of other addictive substances, although it is essential to remember that sugar is a part of many healthy foods like fruits and dairy. Thus, the challenge lies in moderating our sugar intake while still enjoying the taste and benefits that moderate sugar consumption can bring to a balanced diet.
Is Sugar Addiction Comparable to Substance Abuse?
While sugar does exhibit some addictive qualities, experts caution against classifying it in the same category as substances like alcohol and nicotine. Research indicates that sugar can activate the brain’s reward pathways similarly to these potent drugs, leading to cravings and habitual consumption. However, the withdrawal symptoms associated with sugar cessation tend to be much milder than those from addictive substances. This distinction is critical in understanding how we approach sugar in our diets and why moderation is more appropriate than complete elimination.
The perspective on sugar addiction becomes even more nuanced when recognizing that sugars are naturally present in whole foods, which are essential for our well-being. As noted by nutrition experts, rather than viewing sugar in totality as an enemy, it is crucial to focus on the types of sugar consumed and their overall health effects. Reducing the amount of added sugars in processed foods while still allowing for natural sugars from fruits can help mitigate cravings and foster healthier eating habits without the extreme measures associated with substance abuse.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Consumption and Cravings
Processed foods are often laden with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them highly palatable and easy to overconsume. This combination not only heightens sugar cravings but can also lead to increased caloric intake and adverse health consequences. Because these foods are designed to be appealing, they can easily lead individuals to develop a habit of relying on sugar-rich snacks and beverages, which could further entrench their cravings.
To combat the negative health effects of processed foods and sugar, it’s important to select whole food options that satisfy sweetness without the drawbacks. Foods such as fruits, whole grains, and dairy provide necessary nutrients and help mitigate the urge for sugary snacks. Additionally, individuals can learn to read food labels carefully to identify hidden sugars and make more informed choices, gradually changing their consumption patterns and ultimately reducing cravings over time.
Addressing the Health Effects of Sugar Consumption
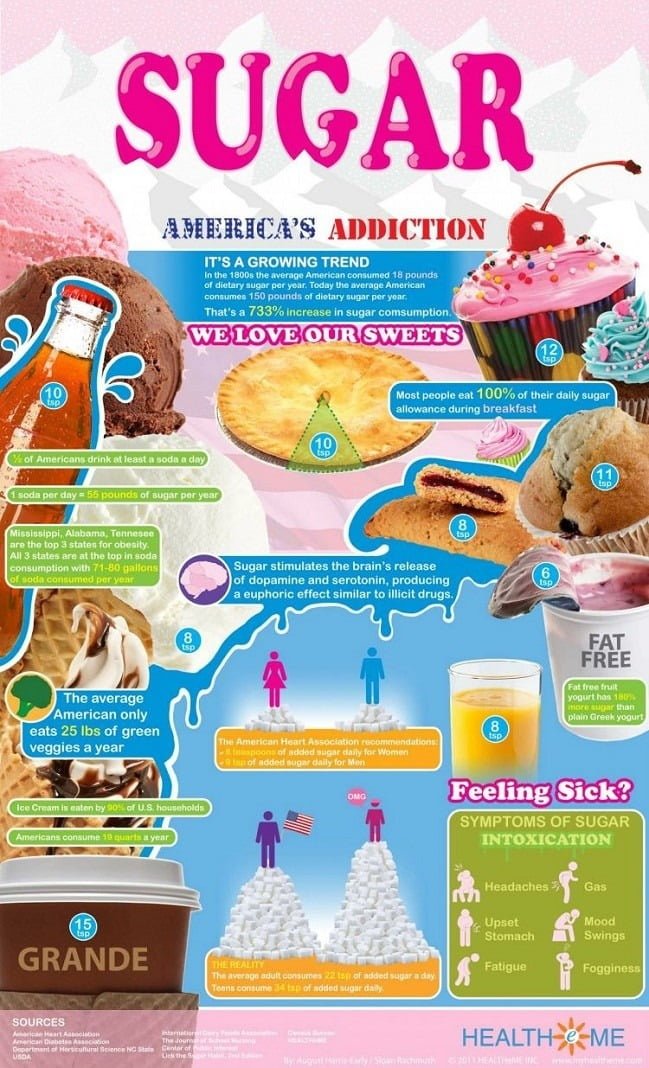
The health effects of excessive sugar consumption are underscored by numerous studies linking high sugar intake to chronic health conditions, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Each year, significant numbers of individuals succumb to illnesses exacerbated by high sugar diets, emphasizing the critical need for awareness regarding sugar consumption levels. For example, the average American consumes around 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which far exceeds the American Heart Association’s recommendations of no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women.
Awareness of personal sugar intake is the first step toward a healthier lifestyle. By educating oneself about hidden sugars in food products, individuals can take proactive measures to reduce their intake and mitigate the associated health risks. This awareness translates into better food choices, promoting the need for nutritional literacy, especially in a food environment dominant with sweetened, processed options.
The Importance of Moderation in Sugar Consumption
Moderation is the key principle when it comes to sugar consumption. While sugar can indeed enhance the flavor and texture of foods, overindulgence can lead to negative health consequences. Finding a balance—wherein one still enjoys sweet treats occasionally while prioritizing whole foods—is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This is particularly important in today’s food landscape, which is filled with overly sweet products that can warp our palates and create unhealthy habits.
Moreover, reducing sugar intake doesn’t have to mean eliminating sweetness from our diets completely. Individuals can explore natural sweeteners or simply enjoy fruits and other healthier alternatives that satisfy their cravings without excess sugar. Gradually reworking one’s diet to prioritize whole foods while being mindful of sugar intake can significantly reduce cravings over time and help individuals maintain a more sustainable and healthful approach to their eating habits.
Cultivating Healthier Eating Habits to Combat Sugar Addiction
To counteract sugar cravings and potential addiction, it’s vital to cultivate healthier eating habits. This involves not only reducing the intake of added sugars but also increasing the consumption of nutrient-dense foods. Incorporating more whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, nuts, and whole grains provides essential vitamins and minerals that can satisfy cravings more healthily. By doing so, individuals can create balanced meals that promote satiety and reduce the desire for excessively sweet options.
Additionally, mindful eating practices can help people better recognize their cravings and the triggers behind them. This involves paying attention to hunger cues and emotional states when reaching for sugary snacks. Developing awareness of one’s eating patterns and making conscious choices helps to diminish the compulsive nature of sugar cravings over time, allowing for a healthier relationship with food.
Recognizing the Psychological Effects of Sugar Consumption
The psychological effects of sugariness can be profound, influencing mood, energy levels, and overall emotional well-being. Many individuals find that consuming high-sugar foods provides a temporary boost in mood or energy, leading to repeated consumption when they seek comfort or a quick energy fix. These cyclical effects can perpetuate the emotional ties we have to sugary treats, making it challenging to alter eating habits.
Understanding these psychological dynamics is crucial for those looking to break free from sugar addiction. Seeking alternatives when reaching for comfort foods, such as engaging in physical activity or finding healthier snacks, can help disrupt the cycle of dependence. Moreover, recognizing the links between sugar consumption and emotions can empower individuals to make more informed and healthy choices, leading to improved mental and physical health.
Reducing Sugar Intake Gradually: Best Practices
For those looking to reduce their sugar intake, a gradual approach is often more effective than going cold turkey, which can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms and increased cravings. Starting with small changes, such as choosing unsweetened versions of products or reducing the amount of sugar added to beverages, allows the palate to adjust to lower levels of sweetness without feeling deprived.
Additionally, substituting with natural sweeteners or incorporating more whole foods can help ease the transition. By focusing on moderation and finding satisfying alternatives, individuals can successfully reduce their sugar consumption over time, leading to better health outcomes without the stress of drastic changes.
The Future of Sugar Consumption and Its Impact on Health
As awareness of the health effects of sugar grows, public health initiatives and food policies are shifting towards promoting healthier eating habits. This includes better labeling of sugary products and educational programs designed to inform consumers about the risks associated with high sugar intake and the benefits of consuming whole, unprocessed foods. The future of sugar consumption will likely see a continued emphasis on moderation and making informed dietary choices.
Moving forward, the focus must remain on encouraging healthier alternatives and supporting individuals in making better choices. With growing advocacy for nutritional transparency and better food options, society can work towards breaking the cycle of sugar addiction and fostering a culture that values nutrition and health, ultimately reducing the associated risks tied to excessive sugar consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addiction a real phenomenon?
The topic of sugar addiction is heavily debated. While sugar isn’t classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, it does trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The accessibility of processed foods rich in sugar can exacerbate these cravings, leading to habitual consumption. Some individuals may even experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they reduce sugar intake, such as headaches and anxiety.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to various health effects, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. While sugar itself is not classified as addictive, high intake from processed foods can lead to a cycle of cravings and compulsive behavior, affecting mental and physical health. Moderation and awareness of sugar intake are crucial for maintaining health.
How can I manage sugar cravings when trying to reduce sugar consumption?
Managing sugar cravings can be challenging. Gradually reducing sugar intake rather than going cold turkey can help mitigate withdrawal symptoms. Incorporating whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide natural sweetness and help satisfy cravings without excessive added sugar. Reading food labels and being mindful of processed foods can also aid in managing sugar consumption.
What role do processed foods play in sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them very palatable and addictive. These foods can lead to increased sugar cravings and habitual consumption. Being aware of the nutritional content of processed foods is essential for managing sugar intake and reducing the risk of developing unhealthy habits.
What is the recommended limit for added sugar consumption?
The American Heart Association recommends that men limit added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons daily, women to 6 teaspoons, and even less for children. Given that the average person in the U.S. consumes around 20 teaspoons daily of added sugar, being mindful of your intake is key to maintaining good health.
Can sugar be part of a healthy diet?
Yes, sugar can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and dairy are beneficial, but it’s crucial to limit added sugars from processed foods, which can lead to health issues. A balanced diet emphasizing whole foods can help incorporate appropriate sugar levels.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar and Addiction | While cravings are real, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol, nicotine, or opiates. |
| Physiological Effects | Sugar can induce withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when eliminated suddenly. |
| Food System Influence | Ultra-processed foods high in sugar are more palatable and lead to habitual consumption. |
| Moderation is Key | Low to moderate sugar intake is generally safe; health consequences arise from excessive consumption. |
| American Heart Association Guidelines | Recommendation: No more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, much less for children. |
| Need for Sugar | Sugar provides flavor and pleasure; it’s part of a balanced diet when consumed appropriately. |
Summary
Sugar addiction is a misunderstood concept; while sugar cravings are real, it does not meet the criteria for addiction in the same way as alcohol or nicotine. Understanding the balance of sugar intake is crucial for maintaining health and preventing overconsumption. Moderate sugar consumption can enhance enjoyment in our diets, so rather than stigmatizing sugar, we should focus on managing our intake to avoid the pitfalls of excessive consumption.